Search
About Fusarium verticillioides 7600
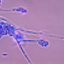
Fusarium verticillioides is the most commonly reported fungal species infecting maize. Fusarium verticillioides is the accepted name of the species, which was also known as Fusarium moniliforme. The species has also been described as mating population A of the Fusarium fujikuroi species complex. F. verticllioides produces the mutagenic chemical compound fusarin C. F. verticillioides produces a group of disease-causing mycotoxins—fumonisins—on infected kernels.
Picture credit: Public domain via Wikimedia Commons (Image source) Taxonomy ID 334819
(Text from Wikipedia.)
More information General information about this species can be found in Wikipedia
Taxonomy ID 334819
Data source Broad Institute
Comparative genomics
What can I find? Homologues, gene trees, and whole genome alignments across multiple species.
 More about comparative analyses
More about comparative analyses
 Phylogenetic overview of gene families
Phylogenetic overview of gene families
 Download alignments (EMF)
Download alignments (EMF)
Variation
This species currently has no variation database. However you can process your own variants using the Variant Effect Predictor:
[]{#other}
Other Data
EST sequences were mapped to the genome using Exonerate.



 Display your data in Ensembl Fungi
Display your data in Ensembl Fungi
 Update your old Ensembl IDs
Update your old Ensembl IDs

![Follow us on Twitter! [twitter logo]](/i/twitter.png)
