Search
About the Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici genome
Fusarium oxysporum comprises a group of soil inhabitants that can exist as saprophytes in the soil debris but also as pervasive plant endophytes colonizing the plant roots. Many strains of these species are pathogenic to plant crops. One of these strains, Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici, is the causal agent of fusarium wilt in tomatoes. The first symptoms of the plant are yellowing and weakness in one side of the plant and progress with wilting of the leaves and browning of the vascular system leading eventually to leaf death and inhability to produce fruits.
The genome sequence, assembly and protein coding genes annotation of the Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici (4287) genome have been generated by the Broad Institute as part of their work on the Fusarium Comparative Sequencing Project. The genome has been sequenced to a coverage of 6x and has a total estimated size of 59.9 Mb represented in 114 scaffolds.
Taxonomy ID 426428
Data source Broad Institute
Comparative genomics
What can I find? Homologues, gene trees, and whole genome alignments across multiple species.
 More about comparative analyses
More about comparative analyses
 Phylogenetic overview of gene families
Phylogenetic overview of gene families
 Download alignments (EMF)
Download alignments (EMF)
Variation
What can I find? Short sequence variants.
 More about variation in Ensembl Fungi
More about variation in Ensembl Fungi
Other Data
- Non coding RNA genes have been annotated using tRNAScan-SE (Lowe, T.M. and Eddy, S.R. 1997), RFAM (Griffiths-Jones et al 2005), and RNAmmer (Lagesen K.,et al 2007); additional analysis tools have also been applied.
- 'Expressed Sequence Tags' (ESTs) from dbEST are aligned to the genome using Exonerate.




 Display your data in Ensembl Fungi
Display your data in Ensembl Fungi
 Update your old Ensembl IDs
Update your old Ensembl IDs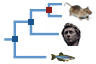

![Follow us on Twitter! [twitter logo]](/i/twitter.png)
